
In order to adapt to the national hazardous waste disposal market demand, as well as to meet the January 1, 2021 promulgation of the new national emission standards ‘Hazardous Waste Incineration Pollutant Control Standards’ GB18484-2020, our company and the relevant design institutes research and development of new technology ------ side blowing submerged combustion melting pool smelting technology to strengthen the melting pool smelting metallurgical technology, after many years of practice, the technology has been developed into a very After years of practice, the technology has developed into a very mature thermal technology system, and has achieved industrial application in the field of non-ferrous metallurgy, such as tin concentrate reduction, direct reduction of liquid lead slag, continuous melting reduction of secondary lead impurities such as lead paste, and treatment of secondary zinc impurities such as zinc leaching slag. In recent years, it has also vigorously promoted the change of technology in the field of industrial hazardous waste disposal and secondary resource recovery.
Industrial hazardous waste disposal has a high melting point, low calorific value, complex composition, unstable incoming material, flue gas contains toxic and harmful components, etc., greatly different from the technology has been the application of cases, the existing, blast furnace, oxygen-enriched side-blowing combustion furnace is difficult to apply to such a working condition. Therefore, the company for the characteristics of the hazardous waste disposal industry, while retaining the technical advantages of the side-blowing submerged combustion furnace, the development and design of a comprehensive recycling treatment furnace, improved technology not only to achieve the purpose of hazardous waste disposal, while making full use of the calorific value of industrial hazardous wastes, but also the recovery of copper and other valuable metals, in line with the concept of green smelting technology.
Background
With the successive introduction of relevant national policies, hazardous waste disposal technology has been developing in the direction of safety, environmental protection and high efficiency.
The first edition of the National Hazardous Waste List was published in 2008, and during the 11th Five-Year Plan period, China's hazardous waste disposal industry began to develop rapidly.
In 2010, a total of 8.4 million tonnes of hazardous wastes were disposed of by hazardous waste operation licence holders nationwide, an increase of 180% compared to 2006.
In 2012, a number of departments jointly issued the ‘Twelfth Five-Year Plan for the Prevention and Control of Hazardous Waste Pollution’, and during the ‘Twelfth Five-Year Plan’ period, the national hazardous waste pollution prevention and control system has been improved, and the utilisation and disposal capacity has been gradually enhanced.
In 2016, the new version of the National Hazardous Waste List was released, and hazardous waste was divided into 46 categories of about 479 kinds, and then many provinces and cities issued the ‘13th Five-Year Plan’ for hazardous waste disposal.
In 2017, the Ministry of Environmental Protection issued the ‘Thirteenth Five-Year’ National Hazardous Waste Management Inspection and Examination Work Programme, vigorously strengthening the prevention and control of hazardous waste pollution.
In 2020, the latest version of the National Hazardous Waste List (2021 Edition) was released. Compared with the 2016 edition, the 2021 edition has further improved and refined the relevant contents into the schedule, indicating that the State has put forward higher requirements for the hazardous waste disposal industry in a more scientific and prudent manner.
The current technologies in the industrial hazardous waste industry mainly include resource utilisation and harmless disposal. The way to achieve hazardous waste resourcefulness is mainly recycling, conversion and incineration to recycle energy in three ways; in terms of harmless disposal technology, the mainstream treatment is incineration disposal method, solidified landfill method, biochemical materialisation method. However, with the continuous growth of the disposal volume and the country's green production requirements continue to improve, the above hazardous waste disposal industry's current technology has been difficult to meet the demand, can not provide effective support for the development of the industry, the upgrading of technology is imperative.
Side Blow Submerged Combustion Melting Pool Melting Technology#Technical Principle#
Side Blow Submerged Combustion Melting Pool Melting Technology introduces the combustion process into the melting pool, where oxygen-enriched air and fuels are sprayed into the melting pool at a speed close to the speed of sound through the side blowing lance, and the fuels are fully combusted inside the melting pool, which directly provides heat for the reaction in the melting pool. At the same time, the gas sprayed into the molten pool by the lance and the gas generated by the combustion of the molten pool to form a stirring, the molten pool to provide good kinetic conditions, thereby accelerating the heat and mass transfer inside the molten pool, so that the heating of the charge, melting, reaction and other processes can be accelerated to complete.
.jpg)
# Technical advantages #
In recent years, the technology has been upgraded in the process of practice, forming a series of unique technical advantages. First, safe and reliable. Furnace body adopts the full-enclosed shell, not easy to gas leakage.
Second, high heat utilisation. The heat intensity per unit volume is large, while sufficient stirring makes the heat and mass transfer in the melting pool occur rapidly.
Third, good environmental protection effect. Adopting micro-negative pressure operation and good sealing of the furnace roof, it can effectively control the low-altitude escape of toxic and harmful gases.
Fourth, high operating rate. The annual operation time of the furnace can reach 300~330d.
#The introduction of hazardous source identification and analysis technology #
At the beginning of 2019, the General Office of the State Council deployed a pilot project for the construction of a ‘waste-free city’, in which one of the main tasks is to improve the risk prevention and control capacity and strengthen the comprehensive safety control of hazardous waste. In order to fundamentally achieve safety control, the technology adopts hazard source identification and analysis technology in the application process to sort out the possible hazard sources of the entire process and core equipment, analyse the hazardous factors and the reasons for the occurrence of hazardous scenarios, assess the risk level, and put forward corresponding protection or control measures. The adoption of hazardous source identification analysis enables safety hazards to be identified and controlled at the source, which greatly improves the safety of this technology in the process of promoting industrial hazardous waste disposal.
# Design features #
The integrated recycling treatment furnace adopts the basic furnace structure of furnace cylinder, enlarged section hearth combined with straight hearth in the rising section, which retains the advantages of side-blowing immersion combustion furnace in terms of high thermal efficiency, high operating rate, high safety, etc.; at the same time, a large number of improvements are made to the furnace body with regard to the unique attributes of hazardous waste disposal.
The comprehensive recycling treatment furnace mainly consists of brick inner liner, water jacket furnace wall, steel plate shell, skeleton, side blowing lance, downward feeding port, metal discharge port, slag discharge port, smoke outlet, electrode and other components, the furnace structure is shown in the figure.
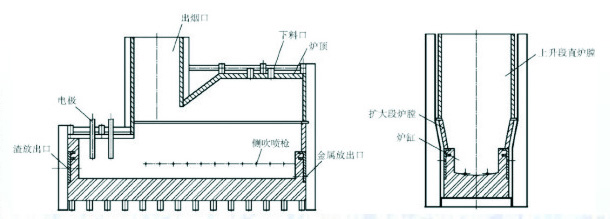
#The #
integrated recycling and treatment furnace in the cylinder area is equipped with an insulated furnace bottom. The bottom layer of the furnace bottom is paved with high alumina bricks, pounded into a reverse arch by magnesium-chromium quality castables, and the upper working layer in direct contact with the molten pool is constructed with high-quality magnesium-chromium bricks.
Side-blowing submerged combustion furnace cylinder four walls using copper water jacket lined with refractory bricks in the form of structure to extend the service life of the brick body, the comprehensive recycling treatment furnace retains this advantage, extending the idea in all around the furnace wall are set up copper water jacket; and in the slag line area will be set in the furnace wall of the copper water jacket two layers of long teeth to increase the cooling area of the fluctuating region of the slag line bricks to strengthen the cooling, to facilitate the hot surface of the wall bricks hanging slag. The lower part of the molten pool is cancelled long teeth, reduce the cooling area, protect the brick body at the same time, reduce the heat loss at the bottom of the cylinder.
In order to ensure that the furnace condition is basically stable, the comprehensive recycling treatment furnace side blowing gun disassembled into oxygen-rich wind side blowing gun and natural gas gun (side blowing gun is the core equipment of the technology, is the company's patented technology). Oxygen-enriched air side blowing gun can provide oxygen-enriched air for the melt pool when in normal use; when it is necessary to strengthen the supplementary heat, it can be directly inserted into the natural gas gun, and when not in use, it can be blocked.
# Expanded section of the furnace #
Due to the slag surface fluctuation range, slag erosive, brick consumption, in order to reduce production costs, in the integrated recycling treatment furnace, the water jacket composite castable structure form instead of refractory bricks. The castables mainly play a protective role in the opening of the furnace, the production process, with the slag scouring, the castables off, relying on the copper water jacket hanging slag operation; in order to increase the cooling intensity, while more convenient to hang the slag, the water jacket hot surface design of a number of grooves.
This type of furnace in the treatment of solid industrial waste at the same time, can also handle waste organic solvents and other combustible liquid industrial waste. Solvent nozzles are installed on the side wall of the expanded section of the furnace body, and the liquid combustible hazardous waste material is sprayed into the high-temperature chamber under high pressure, and the heat released from combustion can feed back into the melt pool.
#The straight hearth in the rising section #
The rising section of the hearth is made of a steel water jacket in combination with castable material, which eliminates the traditional side-blowing furnace chamber lining bricks and reduces the weight of the furnace body considerably. In order to protect the steel water jacket, a specific proportion of high-quality steel fibre reinforced castables are used, while a large number of anchors are welded on the inside of the steel water jacket.
The furnace wall of the enlarged section is inclined at an angle of about 10° to the vertical direction, so that the straight hearth space of the rising section can be enlarged, and at the same time, a large number of secondary air openings are opened on the furnace wall, and oxygen-enriched secondary air is drummed in, so that the incomplete combustion of the CO generated in the molten pool and the reaction, and the CO generated from the combustion of waste organic solvents can be completely combusted in this area.
# Slag depletion area #
hazardous waste material disposal is the most important thing is to come to the material for harmless treatment, in order to ensure that the release of slag after water crushing to become a glassy state of harmless slag, set up a slag depletion area.
The bottom of the furnace in the depletion area adds a layer of anti-arch to prevent the metal phase at the bottom of the melt pool from entering, and a partition wall is set up between the slag pool and the wind mouth area to block the floating material on the slag surface, while slowing down the impact of the side-blowing gun churning power on the slag pool, providing favourable conditions for the further settling and separation of valuable metals in the slag.
Flue gas waste heat recovery
The high temperature flue gas generated by the integrated recovery treatment furnace is cooled by the waste heat boiler, while the heat of the flue gas is recovered and utilised by the waste heat boiler, and SNCR denitrification process is set up in the high temperature section of the waste heat boiler to eliminate the NO.
Quench cooling, dust collection
In order to reduce dioxin re-generation in the process of flue gas treatment, water spray quench cooling is adopted to quench the temperature of the flue gas from 500 ℃ to 200 ℃, and then send the flue gas into the electrostatic dust collector. The flue gas is then fed into an electrostatic precipitator. The flue gas collected by the electrostatic precipitator and quenching tower is returned to the integrated recycling furnace dosage through mechanical ash transport to meet the environmental requirements while maximising the recovery of valuable elements.
Semi-dry desulphurisation
After dust collection, the flue gas is desulphurised using a two-stage, dense-phase, semi-dry tower desulphurisation process to reduce the sulphur content of the flue gas and the acid dew point.
Dioxin removal
Activated carbon is added to the flue gas after semi-dry FGD for decomposition of a small amount of residual dioxin to reduce the dioxin concentration to less than 0.5 TEQng/m³, and the activated carbon is collected through a dioxin trap for recycling.
Wet desulphurisation, temperature rise and whitening, and discharge in compliance with the standards
The treated flue gas is sent to wet deep desulphurisation treatment by a fan, and the emission concentration of each pollutant in the discharged desulphurisation tail gas, environmental protection flue gas, dust-containing waste gas and acid mist-containing waste gas is lower than that of the ‘Pollution Control Standards for Incineration of Hazardous Wastes’.
Products
The molten metal produced is regularly released through the metal discharge outlet and cast into metal ingots. The melting slag is turned into glassy harmless slag through the water crushing system. The glassy harmless slag belongs to the general solid waste, which is transported out by car for external sale.
At present, the company has applied this technology in dozens of industrial hazardous waste disposal and comprehensive secondary resource recovery projects, and designed dozens of comprehensive recovery and treatment furnaces with different specifications and structures for different kinds of industrial hazardous wastes to be processed (covering copper-containing wastes, chromium-containing wastes, electroplating sludge, organic sludge, organic solvents, waste circuit boards, waste activated carbon, and many other categories).